River national nature reserve is eroding areas shrink by half by sewage | | Yangtze River finless porpoises _ news
Original title: pollution not only finless porpoises live in protected areas, please?
Due to the massive sewage around the factory, protected area of more than 70,000 acres shrunk to more than 30,000 acres; there are only 2 technicians, to deal with "water where, it tube where" management trouble ... ... Yangtze River a national finless porpoise faced "foreign invasion", becomes a microcosm of the ecological protection of the Yangtze River tide.
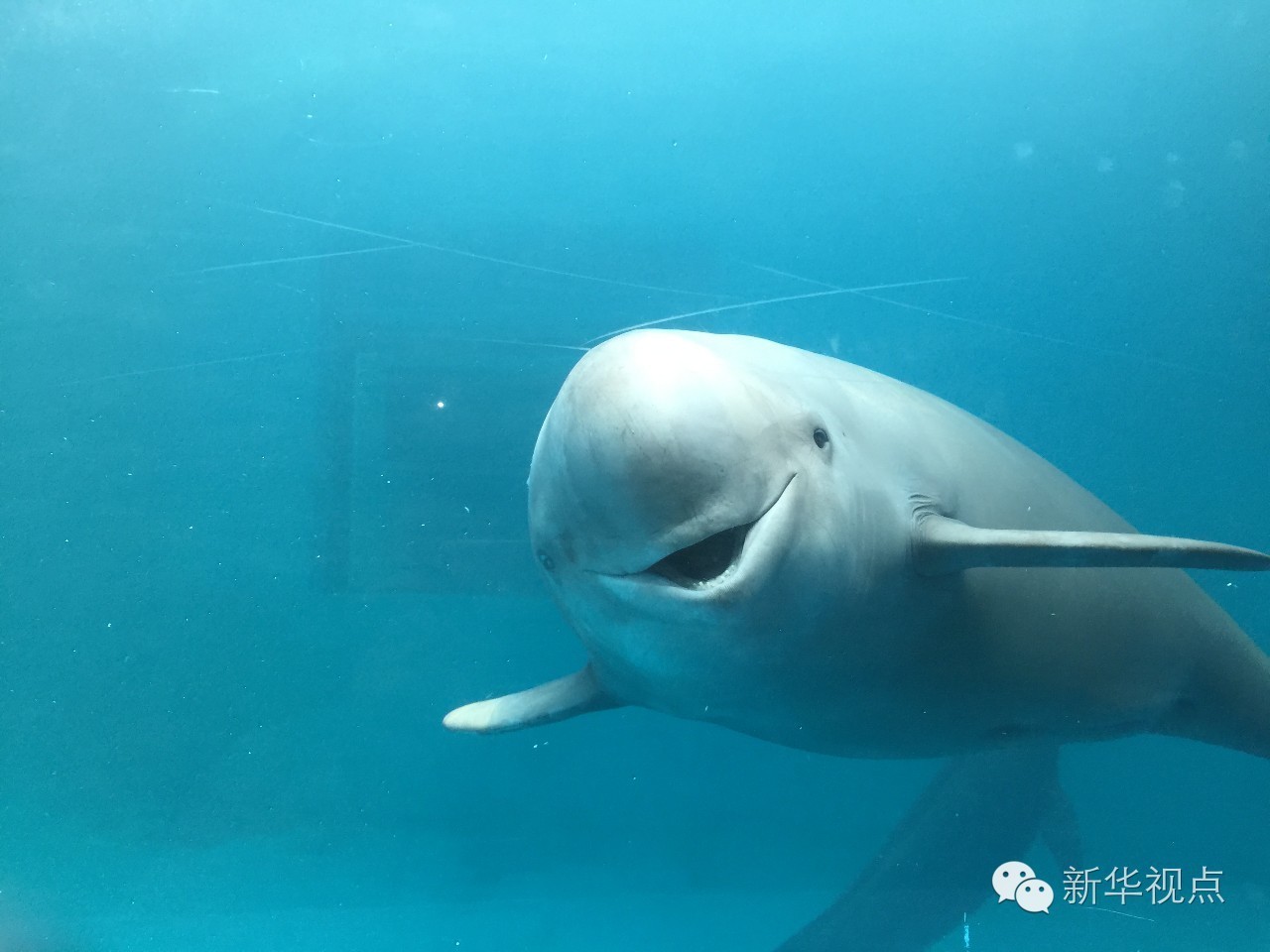 Ex situ conservation of porpoises. Xinhua Cheng Min photography
Ex situ conservation of porpoises. Xinhua Cheng Min photography Plant blowdown "erode" plan "more than 70,000 acres shrunk to more than 30,000 acres"
Well, Hubei Yangtze River Swan Islet in 2016 will increase 9 finless porpoise Dolphin national nature reserve new Member total will be close to 70. But the reporter learned that finless porpoises living environment faces many threats.
Protected areas located in Shishou, Hubei, is the middle reaches of the Yangtze River's only natural conservation and ex situ conservation with State-level nature reserves, protected areas is 21 km of the old course of the Yangtze River finless porpoise natural live place, but the development and operation of protected areas face numerous constraints.
On one hand, pollution of the Yangtze River remains serious, protected areas pollution more than. Chinese Academy of fishery Sciences introduced Wei wei, Chief Scientist, he was investigating a section in the middle reaches of the Yangtze River, coastal cities and factories to Changjiang vertical water. Although it received some treatment, but the effect is still not optimistic. "Industrial sewage outlets along the coast was reported in one or two, but in reality there are hundreds of places. ”
Recent monitoring data from the Yangtze River Water Conservancy Committee showed that sewage emissions increase, increased 29.64 billion tons from 2005 to 2014 33.88 billion tons, an increase of 14.3%. Swan-Zhou said Zhang Zhenhua, Deputy Director, protected areas where poor water quality or even four, five classes of water.
According to the People's Republic of China aquatic wild animals Protection Ordinance, in the nature reserve "core, buffer and experimental zone", banned from production and operation activities, including core prohibiting human activities. Wei wei, Zhang Zhenhua, introduction, not to mention the buffer and experimental zone, even the core business is commonplace.
Zhang Zhenhua, said: "nearly 70,000 acres of protected area planning, but actually contracted to more than 30,000 acres. In addition to agricultural production, a number of local industrial projects ' rushed ' into the protected area. ”
Only 2 technicians monitor the surface protection by "running"
External environmental constraints development of protected areas and protected areas within the development environment is difficult. First is the shortage of professionals and infrastructure backward.
It is understood that the Swan Island area of the reserve is not small, but really only 2 Professional and technical personnel, patrolling, monitoring and management of staff are often overstretched. Swan island is a national nature reserve, but construction of monitoring facilities have not been in place, monitoring protection by "running" management "where water, it tube to which" situation.
Zhang Zhenhua: "ecological conservation is contributing to human beings, did not make a contribution to the local, but also fishermen, restrict industrial projects fall contradictions, and to some extent have local support and cooperation. "As a matter of policy, the fishermen placed is the responsibility of local governments and tasks, but due to poor placement, final trouble falls in protected areas on the head. ”
Meanwhile, water reserves, protected areas have no say. Swan Island protected area in 1998 years ago is communicated with the Yangtze River, after a heavy flood in 1998, was built upstream of the old dikes, blocking the Yangtze River, makes protected areas stagnant water, can only rely on Swan Island gate downstream of drainage or water diversion from the Yangtze River.
"But the essential jurisdiction of the pumping station of water reserves in the hands of local water conservancy departments, every time we go to their water and a water pump. "Zhang Zhenhua said that the protected areas of demand is not the water Department of the primary factors to consider. If the water would flood some farmers illegally for beaches, water if pumping could cause farmers difficulties, so every time the coordination of water reserves are troublesome.
Balancing the relationship between development and environmental protection, increase the intensity of law enforcement
Recently, the State Council Executive meeting adoption of the urban agglomeration in the Yangtze River Delta development plan, required to provide new support for ecological protection. Implementing the ecological construction and restoration works to deepen trans-regional joint air, soil and water pollution treatment, establishment of regional compensation mechanism of ecological protection.
Wei wei, Zhang Zhenhua and other experts, the predicament lies mainly in the local development of the protected areas and ecological protection is inconsistent, law enforcement body is unknown, problems such as insufficient.
They suggest that to strengthen the implementation of relevant environmental protection regulations and policies, and assessment the baton at the same time, speed up the economies of certain cities along the Yangtze River.
Handle the relationship between development and protection. River dolphin protection and to step up publicity to further clarify the subject of law enforcement. Simultaneously, ecological compensation policy, under conditions of moderate introduction of eco-tourism to drive local economic development, harmonization of environmental and economic interests.
Solving development issues within the reserve, also required countries to increase conservation funding and policy input. Want with modern remote monitoring facilities, accelerate the construction of isolation devices upstream pumping stations, increased identified related legal advocacy on the other, increased establishment, attracting professionals. "For example, the protected areas in urgent need of rescue teams and technicians to rescue its ambition of farmed origin. "Zhang Zhenhua said.
Xinhua News Agency reporter Huang yan, Teng Fei
Responsible editor: Wang Hao
Article keywords:The Yangtze Finless Porpoise
I want feedback
Save a Web page
Xinhua News Agency
长江边国家级保护区被排污蚕食 面积萎缩一半|长江|江豚_新闻资讯
原标题:保护区内污染不止 江豚们活得还好吗?
由于周边工厂大肆排污,保护区面积从7万亩萎缩至3万多亩;仅有2名技术人员,却要面对“水涨到哪儿,则管到哪儿”的管理困境……长江边一个国家级江豚保护区面临“内忧外患”,成为长江生态保护之困的一个缩影。
 迁地保护的江豚。 新华社记者程敏摄
迁地保护的江豚。 新华社记者程敏摄 工厂排污“蚕食” “规划的7万亩萎缩至3万多亩”
顺利的话,湖北长江天鹅洲豚类国家级自然保护区2016年将增加9名江豚新成员,累计总数将接近70头。但是记者走访了解到,江豚的生存环境正面临重重威胁。
保护区位于湖北石首市境内,是目前长江中游唯一的自然保护和迁地保护结合的国家级自然保护区,保护区内21公里的长江故道是江豚自然生息的宝地,但是保护区的建设发展和运行面临各种掣肘。
一方面,长江排污仍然严峻,保护区内污染不止。中国水产科学研究院首席科学家危起伟介绍,他曾在长江中游的一个江段作过调查,沿岸城市和工厂向长江直排污水。虽然现在得到一定治理,但效果仍然不乐观。“沿岸工矿企业的排污口报备的是一两处,但实际上有好几百处。”
来自长江水利委员会的最新监测数据显示,废污水量的排放量逐年增加,从2005年的296.4亿吨增加到2014年的338.8亿吨,增幅14.3%。天鹅洲保护区副主任张振华说,保护区的水质差的地方甚至有四类、五类水。
根据《中华人民共和国水生野生动物保护实施条例》,在自然保护区的“核心区、缓冲区、实验区”,禁止从事生产经营活动,其中核心区禁止人类活动。危起伟、张振华等介绍,且不说缓冲区和实验区,连核心区的生产经营活动也是司空见惯。
张振华说:“保护区的面积规划的接近7万亩,但实际上萎缩到3万多亩。除了农业生产,一些地方工业项目也‘闯’入保护区。”
大水面仅2名技术员 监控防护靠“脚跑眼看”
外部环境掣肘保护区发展的同时,保护区内部发展运行的小环境也是困境重重。首先是专业人员数量不足和基础设施落后。
据了解,天鹅洲保护区的面积不小,但真正的专业技术人员只有2名,巡护、监测、管理等人手常常捉襟见肘。天鹅洲虽是国家级保护区,但是监控设施至今没有建设到位,监控防护基本靠“脚跑眼看”,管理成了“水到哪,管到哪”的局面。
张振华坦言:“维护生态是给人类作贡献,没有给地方作贡献,反而还产生渔民转产、限制工业项目落地等矛盾,一定程度上得不到地方的支持与配合。”按照政策,渔民安置是地方政府的职责和任务,但因安置不力,最后麻烦事就落在保护区头上。”
与此同时,保护区的水量,保护区也没有发言权。天鹅洲保护区在1998年前是与长江连通的,1998年大洪水后,故道的上游修建起了堤防,阻断了长江水,使得保护区成了死水,只能依靠下游的天鹅洲闸排水或者从长江引水。

“但是对于保护区水量至关重要的泵站管辖权在地方水利部门手里,每次都是我们去求他们放水、抽水。”张振华说,保护区的需求并不是水利部门首要考量的因素。如果放水,就会淹掉一些农民违法占用的滩涂,如果抽水可能造成农民取水困难,所以每次协调保护区的水量都大费周章。
平衡发展与环保关系,加大执法力度
近日,国务院常务会议通过《长江三角洲城市群发展规划》,要求以生态保护提供发展新支撑。实施生态建设与修复工程,深化大气、土壤和水污染跨区域联防联治,建立地区间生态保护补偿机制。
在危起伟、张振华等专家看来,保护区面临的困境主要在于地方发展与生态保护不相协调,执法主体不明、执法力度不够等问题。
他们建议,加强落实相关生态保护法规政策,同时调整考核指挥棒,加快沿江城市经济转型。
处理好发展与保护的关系。对于江豚保护,要加大宣传力度,进一步明确执法主体。同时匹配生态补偿政策,有条件的情况下,适度引入生态旅游,带动地方经济发展,协调环境和经济利益。
解决保护区内部发展问题,还需国家加大生态保护资金和政策的投入。一方面希望配备现代化远程监控设施,加快建设上游泵站、设立隔离装置,增加相关法律宣传标识等;另一方面,增加编制,吸引专业人才。“例如,保护区急需救护队,让搞养殖出身的技术人员去搞救护有些力不从心。”张振华说。
新华社记者黄艳、滕菲
责任编辑:王浩成
文章关键词: 长江 江豚
新华社